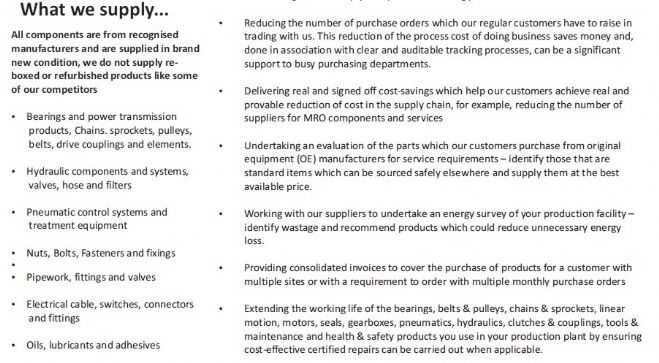
Single Source Supplier

.jpg)

 Consignment Stock
Consignment Stock
Consignment stock is goods which are stored at one location, such as a business or a warehouse, but are legally owned by a different company such as a supplier. Consignment inventory is very common in manufacturing, such as the auto industry. Stock remains under ownership of the supplier until the customer is ready to use it. The customer is not obliged to pay for these supplied goods until they remove them from their consignment stock. It is at this point that they technically buy the stock. If the stock does not sell or the customer decides that it no longer needs it, then the items that are left over are returned to the legal owner.
Consignment stock is closely related to Stores Inventory Managmenent (or SIM. Since the inventory is still under ownership of the supplier, an immediate invoice is not needed when the stock arrives at its location. Only when the stock is sold will the customer create an accounts payable. The supplier is responsible for crediting a customer’s inventory and debiting their stock.
Why Use Consignment Stock?
In today’s fast-moving business world, the relationship between customers and their suppliers can make all the difference in a successful business plan. In order to stay competitive, customers must work with their suppliers for an arrangement that best suits the customer’s needs. That is the main reason for the consignment stock method.
Consignment stock is often used to make it more convenient for the customer to have their supplies and raw materials close to where they manufacture their products. It is also used to reduce a customer’s total working capital. By having consignment stock on hand, either in a stock room or nearby warehouse, a customer can continue with their manufacturing without interruption.
Functions of Consignment Stock
In Stores Inventory Managment, the supplier oversees a company’s inventory items. But in consignment stock, it is the customer’s responsible to manage it. The customer is in charge or moving stock from storage to production. They are also in charge of keeping up with quantities and in contacting the supplier when stock runs low. They are also responsible to communicating with the supplier about moving the stock around, since the supplier still legally owns the items.
The supplier normally inspects the daily or twice weekly. If there are any errors in invoicing and more consignment stock has been used than recorded, the customer is billed for the usage.
When setting up a contract for consignment stock, the supplier and customer will agree on the terms such as how long the contract will last and what to do with left-over consignment. Details are recorded on estimated usage and reorder quantities. Consignment stock contracts can vary in several ways.
Advantages of Consignment Stock
Dealing with consignment stock has many advantages. For instance, the customer knows that raw materials will always be readily available. They do not have to worry about hunting for new suppliers every few months. Consignment stock also saves on money that would normally be invested in unused inventory. This helps keep up a positive cash flow for the customer.
Another advantage is that the purchasing of inventory is not tied into re-supplying and waiting for the new stock to arrive. Purchasing is automatic when the items are used. This saves on time.
One of the main benefits of consignment stock is that customers store the consignment goods at their own warehouses. They can access the goods in the consignment warehouse at any time which makes it much more convenient for the customer.
Customers do not get billed up front for the entire stock. They are only billed for the goods when they are removed from the warehouse and only for the actual quantity taken. Capital is increased because there is less money tied up in non-used inventory.
Re-supply of the consignment can be made at convenient and regular times. This keeps production running smoothly and without having to stop.
Dealing in consignment stock prevents customers from being susceptible to what is known as panic buying. This is when there is a change in the market and the customer panics trying to buy (or sell) stock in order to adapt with the change.
© Hydramatic Source And Supply Ltd 2014

.png)

.jpg)